Having a constant cash flow can often be difficult for small and medium businesses. They are likely to have a cash flow shortage when their short term debts or bills exceed the revenue generated from sales.
If these businesses do not receive a significant portion of account receivables on time, they may face a situation where they are unable to fulfill their short-term payables. To prevent this, they choose factoring solutions.
What is Factoring?
Factoring is a type of finance where businesses can sell their accounts receivables to a third party, known as a factor, to meet their short-term liquidity needs.
A business occasionally needs to turn to factoring to help with short-term cash issues. An essential advantage of factoring is that a company can manage its liquidity issues without having to wait two or three months by contacting a financial institution.
What is Advance Factoring?
Advance factoring is when the factor pays the business for the accounts receivables it has purchased before the due date of the payment. Advance factoring can be availed with or without recourse.
Recourse factoring is when the risks associated with the non-payment of the accounts receivables are not transferred to the factor. The firms are responsible for making sure that the payment has been made to the factoring company by its customers.
In the case of advance factoring, both parties can mutually agree if the factoring should be with or without recourse.
In advance factoring, the factor pays just a portion of the entire amount in advance. They pay the remaining amount on the assured payment date. The margin, which ranges from 5% to 25%, is the amount held back and spent after receiving payment from the buyer.
The factor considers the short-term rate, turnover, financial health of the business, among other factors while calculating the interest rate for advance payments made to the company.
Under this method, the buyer may or may not be aware of the factoring arrangement. The payment is made by the business that pays the invoice to the factor as and when the company receives it, in case it is received t earlier than expected.
What is Maturity Factoring?
Maturity factoring is a type of factoring where the business sells its invoice to the factoring company just like advance factoring.
However, the factor pays the client for such invoices on the date of maturity of the invoice, and in some cases even a day later, as opposed to paying immediately. This is also known as collection factoring.
Maturity financing can be availed with recourse, but it is generally availed as non-recourse factoring, i.e., the risk of credit is borne by the factor and not the company.
This type of factoring means that the payment is collected directly from the debtors. The main reason why businesses avail maturity financing is so that they may have the assurance of receiving payment.
The factor handles all aspects of bookkeeping and documenting costs throughout the process. In addition, the factor is liable for covering all losses resulting from bad debts without turning to the seller.
The factor collects fees and only transfers the agreed-upon seller's share of the revenues.
What is the Difference Between Advanced and Maturity Factoring
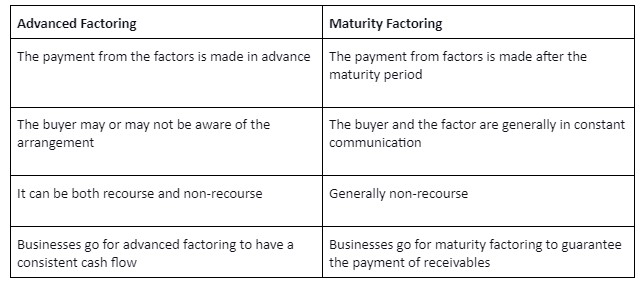
A company can choose between either advance factoring or maturity factoring depending on its needs and priorities. Additionally, there are various other trade finance solutions that companies can consider to satisfy their financial needs.