In the simplest terms, “exports” are the sale of goods or services to a country other than your own. There are 195 countries in the world for you to choose as buyers, but dealing with each of them is a different ballgame entirely. It is easier to trade with certain countries with whom your country has either a multilateral or bilateral trade agreement. These agreements reduce or remove barriers that exist in the trade relationship between countries. Trade agreements foster reciprocal concessions, allow for special favored treatment for exporters from partner countries, and national allowance of non-tariff restrictions.
The Ministry of Commerce and Industry has mentioned on its website that India has 53 concluded or in-progress agreements with countries or group of countries. These agreements present a large pool of nations with whom we have conducive trade relations. As an exporter, there are several factors that could contribute to your choice of export market: tradition - which countries are, traditionally, our big buyers; demand - which countries or regions are likely to seek your products; geopolitical climate - how favorable is the political environment of your selected market, etc. Below we discuss some of these considerations in greater detail.
The Product
It is the most critical factor in deciding the export market. Select a market keeping the demand for your export product in mind. The product should address the need and requirement of the consumers. Also have a look at the product’s historical and recent performance and trends.
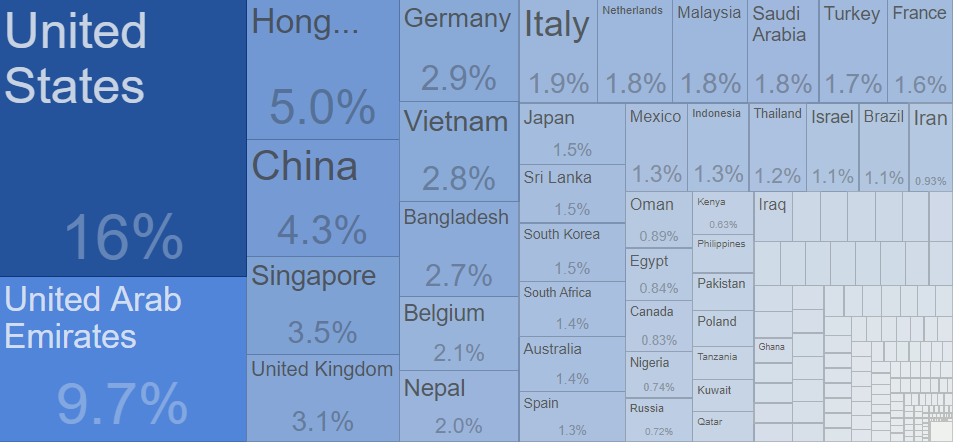
Source: TradingEconomics
For example, as seen in the image above, the USA is India’s largest customer, and in 2017, 45-50% of our exports to them consisted of precious metals and stones, pharmaceutical items, heavy machinery, textiles, and fish. In other words, if you are a fish exporter, the USA is potentially a good market (US$1.7 billion in 2017).
Also Read: How to Find Buyers For Your Export Business
Market Performance
A country might have a massive market for your export product, but take a closer look. Has there been any growth in the market in recent times? Take the example of another country with a comparatively smaller, but exponentially growing, market. Tradition would dictate the first market, whereas, actually, market performance is better in the latter and shows more promise for the future. This would then make the second market a better choice. Remember, it is important to look at future market performance when considering options.
Demand Certainty
You can be sure about consistent demand for your product in a particular market when you know that the local producers are not able to meet the demand or if there is no production in the country. Demand certainty is a precondition for the growth and sustainability of your export business, as it guarantees continued purchases of your exports.
Presence of Trade Barriers
You should also consider the barriers that you will have to overcome to enter a specific market. These could be tariffs and trade restrictions, licensing requirements, government regulations, high-quality parameters, logistical issues, even sudden prohibitions, etc. This is where bilateral or multilateral agreements are important, as countries can agree to make trade easier through measures like mutua infrastructural development and regulatory relaxations. Especially given the recent international geopolitical climate of protectionism, a country’s openness towards international trade is an important consideration for an exporter.
Also Read: How To Open A Current Account For Exports
Relative Profitability
Apart from the per unit selling price, the volume of sales and the incidental expenses will determine the profitability of a product. When you are selling your product to a particular export market, you must consider the price consumers are willing to pay, and the demand for the product. This will help you get a clear understanding of how much product you can send to a particular market, at what price, and thus your likely earnings from the market. Other factors like distance, time and effort required for logistics, travel costs, tariffs etc, will also significantly affect your profitability.
Political and Economic Environment
Examine the legal practices, safety and environmental regulations, commercial laws, etc. of the country whose market you are targeting to ensure that doing business with it doesn’t harm your business interests. Unpredictable political scenarios, confusing ideologies, and economic stress can harm your export business in a particular country in the long run.
Competition
You will likely have existing players selling the same product in the market, or emerging suppliers developing the export product domestically. Too much competition can mean oversaturation of the market, which will affect your market share and profitability. Besides, you also lose the first-mover advantage. Hence, it is important to find out the market share of your competitors and their global presence, to gauge precisely what you are up against.
Incentives
The destination country may have incentives to welcome the inflow of specific items to meet domestic scarcity. India also offers promotional schemes on specific products and services via the Merchandise Exports from India Scheme to incentivize key exports to certain markets. This can be a big advantage if exploited correctly.
Prospect vs Proximity
Exporting to a geographically closer market can make sense for a number of reasons, starting with it being easier to deliver goods. However, a more promising market situated at a greater distance can sometimes be more lucrative for the exporter. Thus, for Indian exporters, exporting to Bangladesh and Pakistan may be easy because of the cultural similarity and proximity, but the sheer volume and potential of the Chinese market makes it a more tempting prospect, in spite of being comparatively far. Depending on your product and growth plans, be sure to consider the balance between prospect and proximity before choosing a market.
Choosing the right market for your products will determine the volume of shipments you can make and the subsequent revenue you will earn. Common sense would dictate that large conventional developed markets like the US or Europe would be safe bets for early-stage exporters; however, there may be more lucrative profits in store in slightly less-crowded but riskier markets. Be sure to conduct your research thoroughly before making your choice, and don't hesitate to pull out if the market becomes too hostile. Good luck!
Also Read: How To Get Your IEC Code
Pro-tips
Thorough research and accurate information are key to finalizing a market. Try to get hold of as much information and statistics from trusted sources as you can.
It is wise to shortlist multiple options and compare them on all parameters before making a final choice.
Don’t forget to consider and finalize logistics firmly before committing to the market.
Neither volume nor profit should be seen in isolation while finalizing the market.
Warnings
Numbers are not always clinching evidence -- confidence in your product can sometimes be the crucial deciding factor in your choice..
Identify and consider all local costs before finalizing the market, as they will be expenses to be incurred irrespective of where you ship goods.
As a beginner, it may be unmanageable to ship to a large number of countries, no matter the temptation. Start small with a couple of markets, and work your way up to geographical expansion from there.




